Ola: Pushing the Frontiers of Omni-Modal Language Model with Progressive Modality Alignment
Recent advances in large language models, particularly following GPT-4o, have sparked increasing interest in developing omni-modal models capable of understanding more modalities. While some open-source alternatives have emerged, there is still a notable lag behind specialized single-modality models in performance. In this paper, we present Ola, an Omni-modal language model that achieves competitive performance across image, video, and audio understanding compared to specialized counterparts.
Something extraordinary has happened in the world of AI. In just over a year, we've witnessed a revolution in video comprehension that few could have predicted. From simple frame-by-frame analysis to sophisticated real-time video understanding, the pace of innovation has been breathtaking. With the recent releases of Ola and Qwen 2.5VL in late 2024 / early 2025, we're entering an era where enterprise-grade video comprehension can run right on your local hardware.
Enter Ola and Qwen 2.5VL
Now, in early 2025, we're seeing the culmination of this rapid evolution with two groundbreaking releases. Ola and Qwen 2.5VL represent different but equally impressive approaches to local video comprehension.
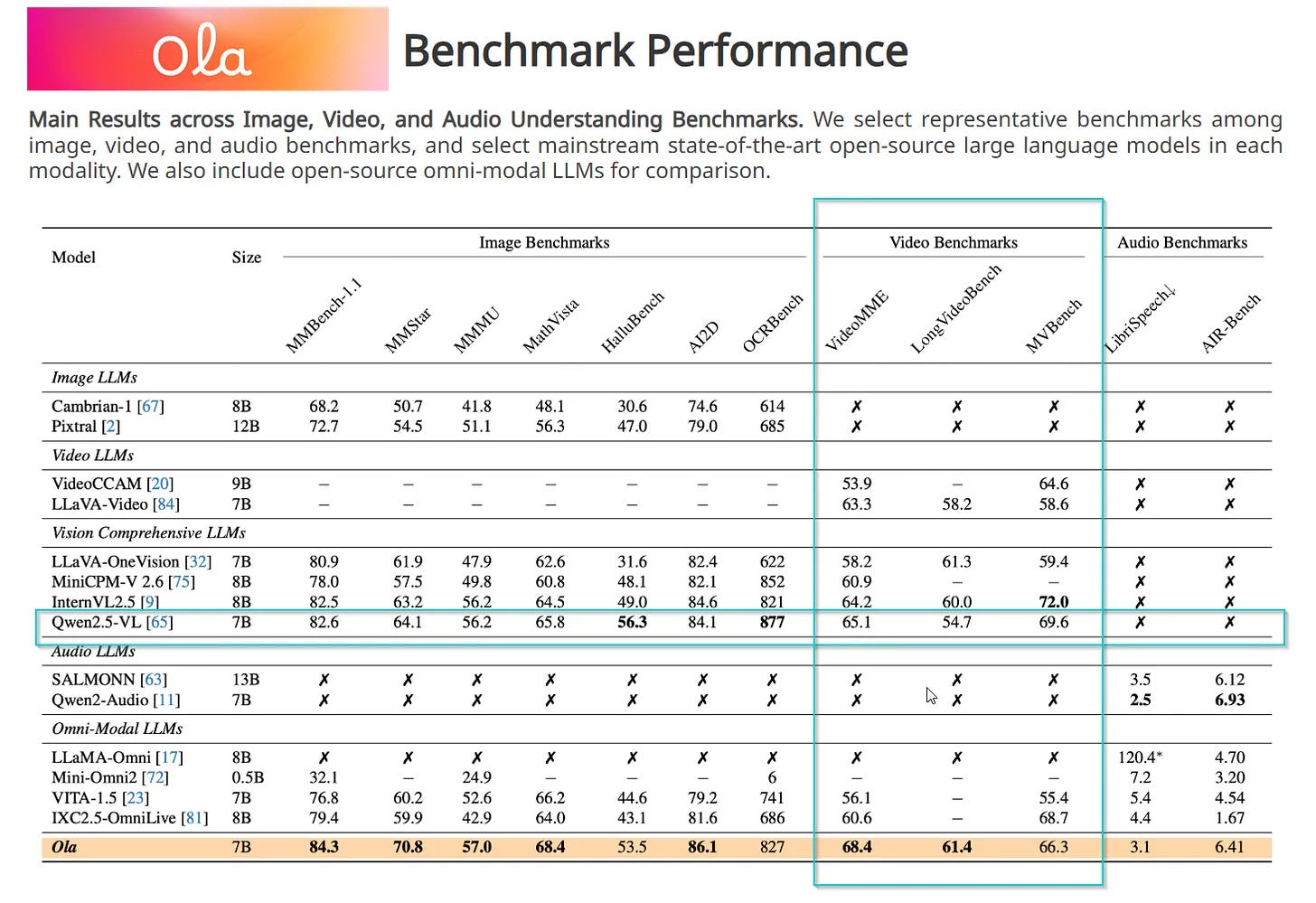
Ola brings us a unified approach to audio-visual processing in a surprisingly efficient 7B parameter model. It's not just about watching videos—it's about understanding them in real-time, processing both visual and audio information in a way that feels natural and responsive.
Qwen 2.5VL takes a different path, leveraging its 72B parameters to achieve deeper understanding and analysis. It excels at complex scene comprehension and can process longer video contexts with impressive accuracy.
The Promise and the Reality
The emergence of these models promises to democratize video comprehension in ways we couldn't imagine just months ago. The ability to run these capabilities locally opens up new possibilities for privacy-sensitive applications, real-time processing, and edge computing scenarios.
However, it's important to note that we're still in the early days of this revolution. In our upcoming series of posts, we'll be diving deep into the practical aspects of running both Ola and Qwen 2.5VL locally. We'll share our hands-on experiences, challenges, and solutions as we work to get these models up and running in real-world scenarios.
Looking Ahead
This is just the beginning. The fact that we've seen such dramatic progress in barely a year suggests we're at the start of something much bigger. As these models mature and new innovations emerge, we expect to see even more impressive capabilities become available for local deployment.
I’ll continue to explore video comprehension with these and newer models as well:
Setup guides for running Ola and Qwen 2.5VL locally
Practical performance comparisons and benchmarks
Real-world application scenarios and limitations
Tips and tricks for optimal deployment
Stay tuned as we continue to document this exciting journey into the future of local video comprehension.
The ability to run sophisticated video comprehension locally isn't just a technical achievement—it's a fundamental shift in how we can approach AI integration in our applications and workflows. Whether you're looking to analyze security footage, process educational content, or build interactive video experiences, these new models open up possibilities that were out of reach just months ago.
We're excited to be part of this journey and look forward to sharing our hands-on experiences with these groundbreaking models in the coming weeks.